There are a lot of folks out there that are intimidated by electricity, let alone the automobile electrical system. To bring some clarity to the mystery, let’s dive right into the basics.
What are the main components of a car electrical system?
Here’s a short breakdown of an automobile electrical system to get us started. The main components of the system are:
- Battery, the primary power source.
- Alternator, recharges the battery and also powers the electrical system while the engine is running.
- Starter Motor, the starter turns the engine over when attempting to start the vehicle.
- Wiring harness, the harness connects the electrical components.
- Fuses, the fuses protect the electrical system from overloads and possible electrical fires.
Probably the two most overlooked things are clean 12-volt power and good ground. Most components, MSD ignition, stereo, amplifier etc. usually call for clean 12-volt power, meaning that 12 volts, not nine for example, is supplied directly to the specific component. Quite often this requires running the wiring directly to the battery. Grounding is the other common issue. When connecting a ground wire, it has to attach to a clean, unpainted, rust-free surface somewhere on the vehicle. Clean grounding will ensure that we have the required clean 12-volts needed. If we attach the ground wire to paint or rust, this does not achieve a perfect ground. The alternator is sometimes also overlooked as we add more and more accessories to a vehicle such as cooling fans, radios, fuel pumps, and such. The more accessories we install, the more of a load on the system, thus requiring higher output alternators.
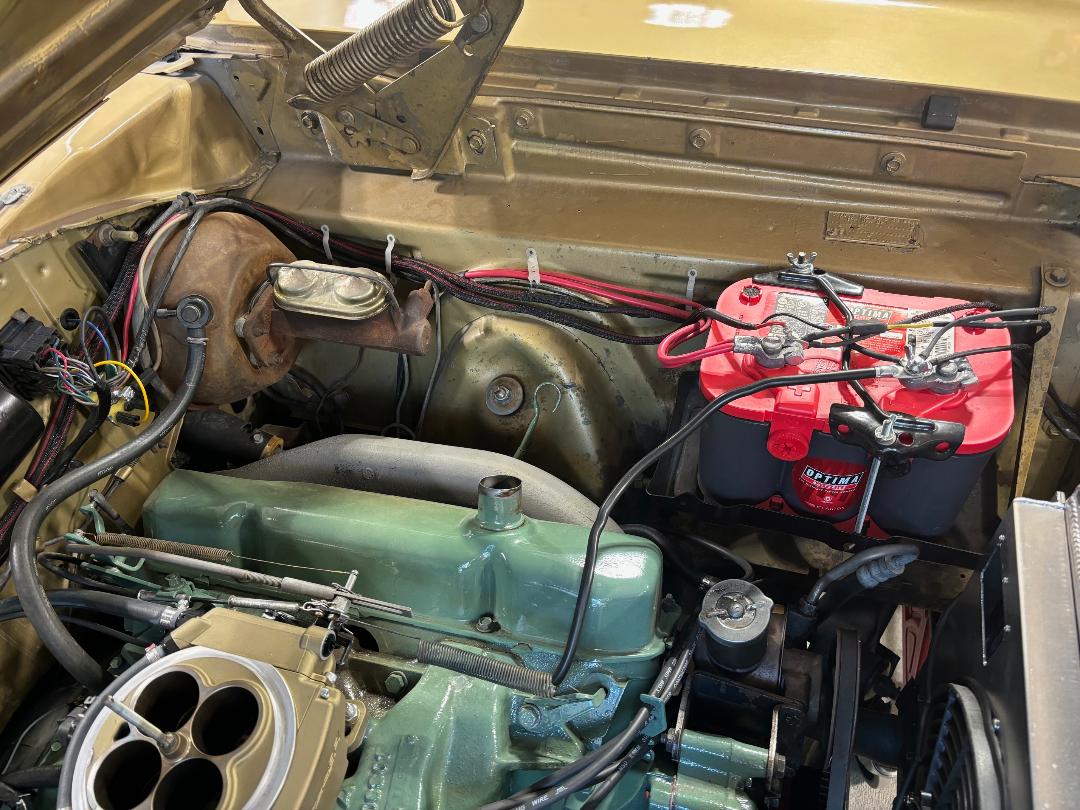

What is a good alternator?
Most modern vehicle alternators run upwards of 200-amps, however, upsizing an alternator too far can also be problematic if the wiring cannot handle the increased load.
Automotive wire size is measured in AWG (American Wire Gauge). The smaller the AWG number, the larger the wire size (diameter), and the larger the AWG number, the smaller the wire size. Therefore, 22 AWG is smaller than 10 AWG. The key factor in determining wire size is the wire’s current-carrying capacity. Wire should be sized to handle more current than a particular fuse to ensure the fuse blows (fails) before the wire overheats or melts. Wiring should also be of different colors as this will make any future troubleshooting so much easier.
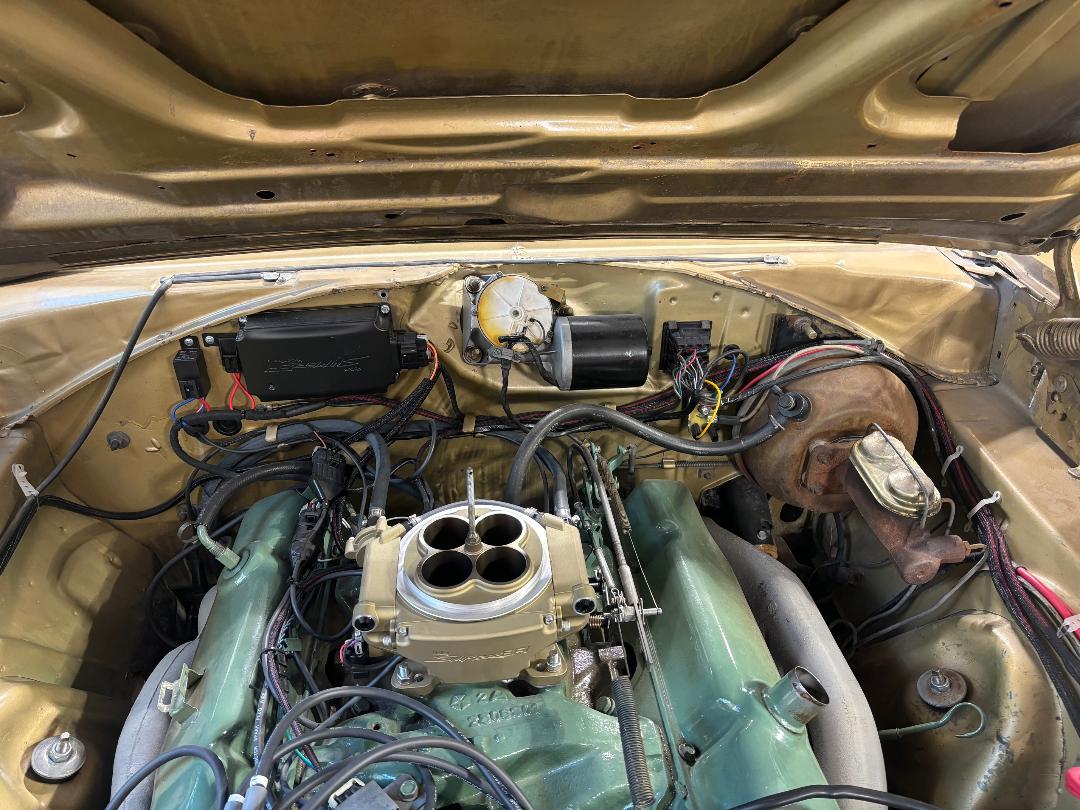

What does a fuse do?
Fuses are used to protect the car’s wiring system from excessive current that can lead to component damage and electrical fire. When the current passing thru a fuse exceeds the amperage the fuse is designed for, the fuse will fail internally, thus preventing any damage to the wiring. Using too small a fuse and you will constantly be blowing fuses; conversely, using too large a fuse allows too much current to pass through the fuse, allowing the wires to heat up and possibly catch fire. The manufacturer of each specific component will recommend the size fuse that you should use and the wiring needs to be sized accordingly.
I have found when installing something on one of my builds that it is usually easier to mount the device in the desired location first and then run the wiring accordingly, whether using a provided harness or you are building your own. This allows for a cleaner look when running wires. Few things are as unsightly on a beautiful car than when you open the hood and the wiring looks like a rat’s nest. There is so much information available on the web these days that any of us can make electrical work fairly painlessly and look beautiful.
By Chris Ochs